Initiatives for Climate Change
NBF's perception of climate change
In December 2015, the Paris Agreement was adopted at the twenty-first session of the Conference of the Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (COP21) as a new international framework for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and such after 2020. The agreement upheld a goal to keep the global average temperature increase well below 2℃ compared with the pre-industrial levels, as well as another goal to make the best efforts to limit the increase to 1.5℃.
NBF has positioned conducting business that reduces energy consumption and greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions to curb global warming and lower the risks associated with climate change as its social mission in carrying out real estate investment management business, and set such as one of the material issues (Materiality).
Support for TCFD (Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures)
NBFM expressed support for the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) in 2021 to promote disclosure on climate-related issues. In addition to endorsing the TCFD, NBFM also joined the TCFD Consortium. The TCFD Consortium, in which many companies and organizations in Japan supporting the TCFD participate, discusses how information on climate-related issues should be disclosed and how it should be used. NBFM will continue to promote the disclosure of relevant information based on analysis of the risks and opportunities that climate change poses to its business and finances.

Governance
In accordance with the “Regulations Concerning ESG Initiatives,” NBFM has organized the ESG Promotion Committee, with the President and CEO of NBFM as the final decision-making authority. The committee makes decisions on identification, assessment and management of risks and opportunities related to climate change, which is an ESG issue, implementation of measures to mitigate risks, and setting targets and KPIs. Furthermore, NBF and NBFM’s Boards of Directors receive reports from the ESG Promotion Committee on resolutions on climate-related issues and the progress of initiatives and review the risk management process and give instructions on new actions as necessary.
For details on NBFM's ESG promotion system, please refer to ESG Promotion System.
Strategy
Scope and assumptions of scenario analysis
In the scenario analysis conducted in this study, all assets held by NBF were considered.
NBF refers to the following scenarios in its scenario analysis. In addition, each scenario assumes the following outlook on the world.
| Classification | Scenario overview | Main reference scenarios |
|---|---|---|
| 4℃ scenario |
A scenario in which temperatures are assumed to rise by 4℃ compared with pre-industrial levels. Climate change will progress without sufficient progress towards global decarbonization, and disasters will become more intense and physical risks greater than in the current world. Transition risks, such as tighter laws and regulations, will be relatively small, but there are concerns about increased air conditioning costs in offices and increased costs of preparing for more severe extreme weather events. |
|
| 1.5℃ scenario |
A scenario in which temperatures are assumed to rise by 1.5℃ compared with pre-industrial levels. While physical risks will remain relatively small as the world deepens its efforts to decarbonize, the legal and other risks associated with pressing ahead with such efforts will be greater and more severe than at present. Specifically, while costs associated with taxing GHG emissions from offices are likely to increase, business opportunities include higher rents for properties with high environmental performance. |
|
Identifying risks and opportunities, assessing financial impact and initiatives
NBF has identified the risks and opportunities related to its real estate investment management business while referring to each of the abovementioned scenarios and analyzed and evaluated their business and financial impacts as follows.
Based on such results, to mitigate risks and realize opportunities, NBF will implement various initiatives including the following.
| Risks | Minor | Moderate | Major | |||||
| Opportuniteis | Minor | Moderate | Major | |||||
| Category | Principal risks and opportunities | Factors that may affect business and financial performance | Financial impact (Millions of JPY) | Risk management, countermeasures, initiatives | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4℃ Scenario | 1.5℃ Scenario | |||||||
| Mid-term 2030 |
Long-term 2050 |
Mid-term 2030 |
Long-term 2050 |
|||||
| Transition Risks | Policy and Legal | Introduction of GHG emissions regulations Introduction of carbon taxes |
Increase in costs due to responding to legal regulations(※) | ー | ー | 960 | 1,270 |
|
| Strengthening of energy conservation standards | Increase in renovation costs to improve energy efficiency(※) | ー | ー | 8,070 | 3,010 |
|
||
| Increase in property acquisition prices due to scarcity of investment targets | ー | ー | ー | ー |
|
|||
| Technology | Dissemination of new technologies related to environmental performance | |||||||
| Increase in renovation costs due to introduction of new technologies | ー | ー | 250 | 70 |
|
|||
| Market | Changes in environmental performance values in financing | Increase in financing costs for properties with relatively low environmental performance | ー | ー | 2 | 10 |
|
|
| Change in tenants' needs for environmental performance | Decrease in rental income from properties with relatively low environmental performance | ー | ー | 90 | 90 |
|
||
| Reputation | Decrease in corporate (brand) value due to delayed response to climate change | Decrease in rental income (due to decline in brand strength) | ||||||
| Physical Risks | Acute | Increase in the severity of extreme weather (Typhoons, floods, and heavy rains) |
Increase in costs of countermeasures | 5 | 1 | ー | ー |
|
| Decrease in operating revenue at the time of damage | 560 | 560 | ー | ー |
|
|||
| Incurring recovery costs when damage occurs | 2,560 | 2,560 | ー | ー |
|
|||
| Chronic | Rising sea levels | Increase in costs of countermeasures | ー | ー | ー | ー |
|
|
| Rising average temperatures | Increase in costs due to increased air-conditioning load | 170 | 520 | 140 | 200 |
|
||
| Opportunities | Resource Efficiency | Installation of high efficiency facilities | Reduction of utility costs | ー | ー | 580 | 580 |
|
| Products and Services | Appealing to tenants and occupants by providing low emission facilities and services | Increase in income from attracting tenants/occupants | ー | ー | 4,500 | 6,000 |
|
|
| Markets | Continuous offering of rental properties that meet the changing preferences of tenants and occupants Development of new customer base |
|||||||
| Development of new investor base | Increase in the amount of financing and decrease in financing costs by responding and appealing to investors who place importance on addressing climate change issues | ー | ー | 5 | 20 |
|
||
| Resilience | Improvement of adaptability to climate-related risks by improving disaster prevention performance | Improvement of resilience to natural disasters by improving disaster prevention performance | 210 | 210 | ー | ー |
|
|
- Evaluation and analysis using Carbon Risk Real Estate Monitor (CRREM) have been implemented for part of the transition risks.
As for the 1.5℃ scenario with a relatively high probability, which NBF should aim for, a chart of the increase/decrease in financial impact has been made as follows. Despite the increase in expenses for energy-saving renovations and response to laws and regulations, opportunities for a positive financial impact are believed to arise with the enhancement of competitiveness in terms of leasing through the implementation of initiatives. Therefore, such scenario is evaluated as a positive scenario as a result of comprehensively taking such factors into account.
1.5℃ Long-term 2050 Estimated Business and Financial Impact
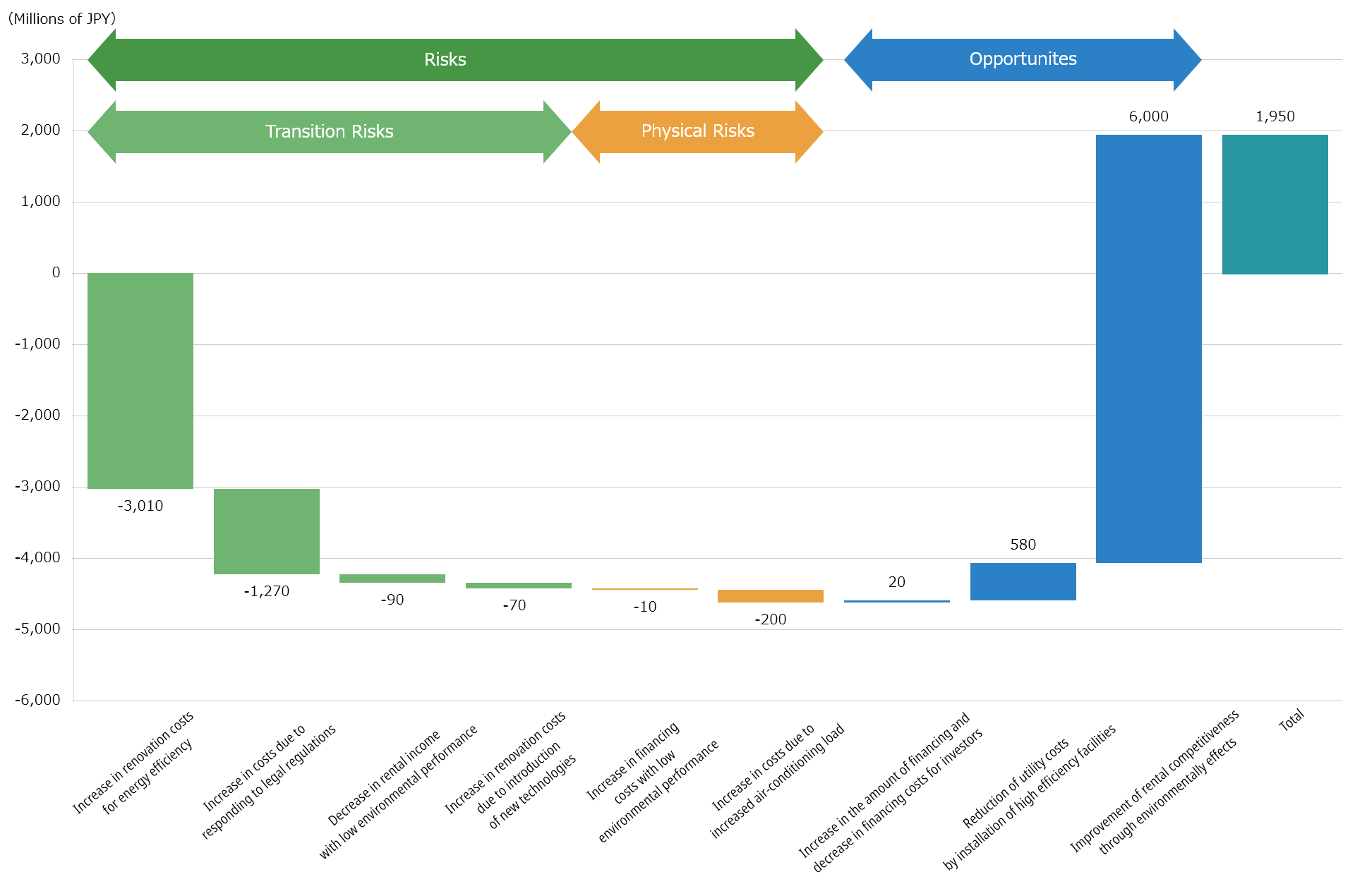
- The qualitative assessment shows the annual amount of impact estimated in reference to the scenarios presented by major institutions, etc. based on NBF’s portfolio, operational performance, etc., and does not guarantee the accuracy of the figures. In addition, the assumed countermeasures are assumptions used in the estimation and their execution has not been planned or decided.
● Transition risks
In order to achieve the Paris Agreement and the Glasgow Climate Pact's non-binding target of limiting the global average temperature increase to 1.5℃ compared with pre-industrial levels, as well as Japan's "carbon neutrality by 2050," curbing greenhouse gas emissions is an urgent issue.
NBF has made the following efforts as part of the method to achieve the numerical target established by setting the reduction of GHG emissions as the main materiality assuming that the transition to a decarbonized society will strengthen policies and regulations, accelerate innovation, change the behavior of all parties in the office leasing business, and such.
- Systematic implementation of energy-saving renovation plans
NBF has set a goal of “reducing energy-derived CO2 emissions by 46% or more by 2030 (compared with 2013 levels),” and is working to promote LED lighting and introduce high-efficient equipment based on energy-saving renovation plans for the properties it owns. In addition, there are 14 properties (approximately 21% of the portfolio based on the number of properties as of the end of December 2024) that are subject to the total volume control (Tokyo Cap-and-Trade Program), which imposes the reduction of GHG emissions from large-scale business facilities in Tokyo, and NBF is considering and promoting plans to achieve an average of 50% reduction between 2025 and 2029. For properties that underwent energy-saving renovation, NBF examines their effects as necessary. - Introduction of electricity derived from renewable energy sources
By promoting the greening of electricity used in common and tenant areas of its owned properties, NBF aims to reduce GHG emissions from the properties it owns as well as meet the needs of its corporate tenants for purchasing green electricity. - Building of a portfolio with superior environmental performance
NBF is building a portfolio with superior environmental performance by proactively acquiring properties developed in consideration of the reduction of environmental load and energy saving and properties with high environmental efficiency (properties reducing energy consumption and emitting less GHG, etc.). - Introduction of Internal Carbon Pricing (ICP)
NBF has set a price per ton of CO2 (20,000 yen/t-CO2) and estimates the amount of CO2 emissions generated and reduced in environmental-related projects, such as LED replacement, in order to conduct economic evaluations that consider CO2 emissions related to investments and make use of this as a reference for making decisions on whether to proceed with the projects.
● Physical risks
Climate change is causing average temperatures and sea levels to rise around the world, and damage from rising average temperatures, heavy rainfall, typhoons, etc. has been observed in Japan as well. With the progression of global warming, the risk of natural disasters becoming more severe is expected to further increase in the future. NBF is taking the following measures to mitigate the risks of the properties it owns, after regularly assessing disaster risks.
- Systematic implementation of building and facility improvements
NBF is installing and improving flood barriers based on a flood countermeasure plan formulated after analyzing flood risks using flood hazard maps. In addition, we are systematically updating and enhancing emergency power generators.

Installation of flood barriers
(NBF Higashi-Ginza Square)

Inspection/update of emergency power generator
(NBF Takanawa Building)

Installation of an additional emergency power generator
(NBF Shibuya Garden Front)
- Preparing for possible disasters
In order to improve resilience, NBF is strengthening its BCP system, placing disaster prevention stockpiles and conducting disaster drills.
NBF has established an advanced emergency communication system with NBF Office Management Ltd., which manages operation of the properties, to quickly identify the extent of the damage.
● Opportunities
The Paris Agreement has triggered a movement to embrace decarbonization as an opportunity for corporate management (decarbonization management), and NBF believes that efforts to mitigate climate change and adapt to change will contribute to the creation of new business opportunities.
NBF is undertaking the following initiatives at its owned properties to mitigate and adapt to climate change, as opportunities to enhance competitiveness in terms of leasing will also arise by responding to transition risks.
- Acquisition of Green Building Certification
Against the backdrop of growing preferences for environmental performance upon leasing offices, NBF has obtained green building certification for all its properties as it views third-party certification regarding the specifications and various initiatives of its owned properties as added value. - Procurement of Green Finance
NBF uses green finance, a method of procuring funds specifically for initiatives that have a positive effect on the environment, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions and investing in renewable energy, and aims to procure more than 10 billion yen annually.
Risk Management
NBFM's processes for managing climate change-related risks pertaining to NBF's real estate investment management business are as follows.
Process for identifying and assessing risks and opportunities
Key risks and opportunities related to climate-related issues are discussed at least once every three months at the ESG Promotion Committee.
Processes for managing risk
The President & CEO, who has the highest responsibility for climate-related issues, instructs the Strategy Planning and ESG Promotion Department to discuss countermeasures for risks identified and assessed at the ESG Promotion Committee at least once every three months. Based on the results of the discussion of countermeasures and their implementation status reported, the Strategy Planning and ESG Promotion Department conducts monitoring (e.g., checking the implementation status against GHG reduction targets, analyzing the reasons for increases or decreases, and considering necessary countermeasures).
Integration into a company-wide risk management program
Climate change-related risks are integrated into the multi-disciplinary company-wide comprehensive risk management process in the same way as other business risks, and are discussed at least once every three months at the Risk Management Meeting.
Please click here for an explanation of the ESG Promotion Committee and the Strategy Planning and ESG Promotion Department.
Metrics and Targets
Please refer to the "Materiality" page for the KPIs and targets that NBF has set in relation to climate change issues for its real estate investment management business (the relevant indicators are "GHG emissions" ,"CO2 emissions intensity", "green building certification coverage" and "procurement of green finance"). Please refer to the following pages for the actual results of each indicator.
- GHG emissions: Environmental Performance
- CO2 emissions intensity: Environmental Performance
- Green building certification coverage: Utilization of Green Building Certification
- Procurement of green finance: Green Finance